Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -ray discrimination based on the property and thickness controls of scintillators using Li glass and LiCAF(Ce) in a
-ray discrimination based on the property and thickness controls of scintillators using Li glass and LiCAF(Ce) in a  -ray field
-ray fieldKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Terasaka, Yuta; Tomita, Hideki*; Yoshihashi, Sachiko*; Yamazaki, Atsushi*; Uritani, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1046, p.167636_1 - 167636_8, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:94.27(Instruments & Instrumentation)We focus on the thickness and property controls of inorganic scintillators used for thermal neutron detection in intense  -ray fields without considering pulse shape discrimination techniques. GS20
-ray fields without considering pulse shape discrimination techniques. GS20 (a lithium glass) and LiCaAlF
(a lithium glass) and LiCaAlF :Ce(LiCAF:Ce) cintillators with thicknesses of 0.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively, have been employed. Pulse signals generated by photomultiplier tubes, to which the scintillators were coupled, were inserted into a digital pulse processing unit with 1 Gsps, and the areas of waveforms were integrated for 360 ns. In a
:Ce(LiCAF:Ce) cintillators with thicknesses of 0.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively, have been employed. Pulse signals generated by photomultiplier tubes, to which the scintillators were coupled, were inserted into a digital pulse processing unit with 1 Gsps, and the areas of waveforms were integrated for 360 ns. In a  Co
Co  -ray field, the neutron detection for GS20
-ray field, the neutron detection for GS20 with a 0.5-mm thickness was possible at dose rates of up to 0.919 Gy/h; however, for LiCAF:Ce, neutron detection was possible at 0.473 Gy/h, and it failed at 0.709 Gy/h. Threfore, in a
with a 0.5-mm thickness was possible at dose rates of up to 0.919 Gy/h; however, for LiCAF:Ce, neutron detection was possible at 0.473 Gy/h, and it failed at 0.709 Gy/h. Threfore, in a  Co
Co  -ray field, the neutron/
-ray field, the neutron/ -ray discrimination of GS20
-ray discrimination of GS20 was better than that of LiCAF:Ce due to its better energy resolution and higher detection efficiency.
was better than that of LiCAF:Ce due to its better energy resolution and higher detection efficiency.
Igarashi, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2020-006, 261 Pages, 2020/09
A literature review was conducted on the increase in surface area of vitrified products of HLW due to the fracturing caused by cooling during glass pouring process and by mechanical impact, from the perspective of a parameter of the radionuclide release model in the performance assessment of geological disposal system studied overseas. The review was focused on the value of surface area increase factor set as a parameter in the model, the experimental work to evaluate an increase in surface area, and how the parameters on surface area were determined based on the experimental results. The surface area obtained from the experiments executed in Japan was also discussed in comparison with the overseas studies. On the basis of the investigation, the effects of various conditions on the surface area were studied, such as a diameter of vitrified product, cooling condition during and after the glass pouring, impact on vitrified products during their handling, environment after the closure of disposal facility, and others. The causes of fracturing are associated with the phenomena or events in the waste management process such as production, transport, storage, and disposal. The surface area increase factors set in the nuclide release model of the glass and their bases were reviewed. In addition, the measured values and the experimental methods for surface increase factors published so far were compared. Accordingly, the methods for measuring surface area as the bases were identified for these factors set in the models. The causes of fracturing and features of these factors were studied with respect to the relation with the waste management process. The results from the review and assessment can contribute to the expanding the knowledge for the conservative and realistic application of these factors to performance assessment, and to the developing and upgrading of safety case as a consequence.
Fukui, Toshiki*; Maki, Takashi*; Miura, Nobuyuki; Tsukada, Takeshi*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 23(2), p.169 - 173, 2016/12
The basic research programs for the next generation vitrification technology, which are commissioned project from Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan, have been implemented from 2014 until 2018 for developing the advanced vitrification technology of low level wastes and high level liquid wastes.
Amamoto, Ippei; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Kitamura, Naoto*; Takebe, Hiromichi*; Mitamura, Naoki*; Tsuzuki, Tatsuya*; Fukayama, Daigen*; Nagano, Yuichi*; Jantzen, T.*; Hack, K.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(10), p.1467 - 1475, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:28.09(Nuclear Science & Technology)The iron phosphate glass (IPG) medium is known to be a high-efficiency glass medium, therefore we try to evaluate its applicability to immobilize sludge bearing radioactive nuclides arising from treatment of contaminated water at the stricken Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. For this study, many physical and chemical properties of target materials are necessary to evaluate the behaviours of IPG medium and its waste forms. Inevitably, it will entail the need for many and varied types of experiments to be carried out under high temperature. It is therefore rational to apply appropriate theoretical analysis first so as to reduce the number of experimental run. For this reason, some necessary thermodynamic values for theoretical analysis were estimated by CALPHAD approach followed by making up the calculated phase diagrams. By comparison with experimental results, they were found to be reliable for evaluating the behaviours of IPG medium and its waste forms.
Yokota, Terufumi
Physica A, 363(2), p.161 - 170, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.77(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Within a class of cluster approximations, the Ising spin glass model on a d-dimensional hypercubic lattice is solved near the spin glass transition temperature. Spin glass order parameter function and Almeida-Thouless line are obtained.
Murakami, Hiroshi
Chemical Physics Letters, 417(4-6), p.550 - 554, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:15.89(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Yokoo, Takeshi*; Nishihara, Kenji; Morita, Yasuji; Ikeda, Takao*; Takaki, Naoyuki*
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
The benefit of implementing Partitioning and Transmutation (P&T) of high-level wastes was parametrically surveyed. The possible reduction of the geological repository area was estimated. By recycling minor actinides (MA), the repository area required for unit spent fuel was reduced significantly in the case of MOX-LWR. This effect was caused by removal of  Am which is a long-term heat source. By partitioning the fission products, in addition to MA recycling, further 70-80% reduction from the MA-recovery case can be expected for both UO
Am which is a long-term heat source. By partitioning the fission products, in addition to MA recycling, further 70-80% reduction from the MA-recovery case can be expected for both UO and MOX. This significant reduction was independent of the cooling time before the partitioning process.
and MOX. This significant reduction was independent of the cooling time before the partitioning process.
Otani, Eiji*; Suzuki, Akio*; Ando, Ryota*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Advances in High-Pressure Technology for Geophysical Applications, p.195 - 209, 2005/09
This paper summarizes the techniques for the viscosity and density measurements of silicate melt and glasses at high pressure and temperature by using the X-ray radiography and absorption techniques in the third generation synchrotron radiation facility, SPring-8, Japan. The falling sphere method using in situ X-ray radiography makes it possible to measure the viscosity of silicate melts to the pressures above 6 GPa at high temperature. We summarize the details of the experimental technique of the viscosity measurement, and the results of the measurements of some silicate melts such as the albite and diopside-jadeite systems. X-ray absorption method is applied to measure the density of the silicate glasses such as the basaltic glass and iron sodium disilicate glass up to 5 GPa at high temperature. A diamond capsule, which is not reactive with the glass, is used for the density measurement of the glasses. The present density measurement of the glasses indicates that this method is useful for measurement of the density of silicate melts at high pressure and temperature.
Katayama, Yoshinori; Inamura, Yasuhiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 238(1-4), p.154 - 159, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:52.8(Instruments & Instrumentation)It is well know that many substances have different structures in the crystalline state and they exhibit first-order structural phase transitions by a change in pressure. On the other hand, pressure-induced structural changes in the liquid and glassy states were supposed to be monotonous. The recent development of synchrotron radiation sources enables us to perform structural studies on liquids and glasses under high pressure and high temperature conditions. These studies revealed that the changes in the liquid and glassy states are not necessarily monotonous. We will present recent results on liquid phosphorus and silica glass.
Yokota, Terufumi
Progress of Theoretical Physics Supplement, (157), p.90 - 93, 2005/06
The mean-field p-state Potts glass model is studied in the presence of a field. As effective ferromagnetic interaction in the Potts glass model grows as temperature decreases, uniform part of the interaction is set to make effective ferromagnetic interaction zero at the continuous glass transition temperature without field. Replica symmetry breaking pattern is obtained analytically near the freezing of the transverse components for small fields. Replica symmetry breaking is continuous for p 3.4, which is similar to the symmetry breaking for the Ising spin glass model. One step replica symmetry breaking is stable for 4.6
3.4, which is similar to the symmetry breaking for the Ising spin glass model. One step replica symmetry breaking is stable for 4.6 p
p 3.4. The transition to the transverse freezing phase is discontinuous for p
3.4. The transition to the transverse freezing phase is discontinuous for p 4.6. This threshold is larger than 4 that is the threshold for the zero field case. These results show that qualitative feature of the transition in a field is similar to that without field if the number of the Potts components is shifted accordingly.
4.6. This threshold is larger than 4 that is the threshold for the zero field case. These results show that qualitative feature of the transition in a field is similar to that without field if the number of the Potts components is shifted accordingly.
Yamauchi, Toshihiko
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 43(9A), p.6473 - 6474, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)The output pattern of He-Ne laser that passes through the optical glass fiber bundle used for free electron laser etc. depends on the weight of load (modulation of transverse mode). The increment of pattern radius exponentially increases with the load. It is considered that the micro bending causes this increment. Next, the estimated delay time also exponentially increases with the weight of load, and the estimated delay time is the extent of pico-second.
 glass under high pressure and temperature
glass under high pressure and temperatureInamura, Yasuhiro*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Utsumi, Wataru; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Physical Review Letters, 93(1), p.015501_1 - 015501_4, 2004/07
Times Cited Count:120 Percentile:93.74(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The temperature dependence of the X-ray structure factor for SiO glass was measured at several pressures up to 19.2 GPa. The position of the first sharp diffraction peak moved to a higher momentum transfer as the temperature increased in a specific pressure-temperature range. The intermediate range structure was thermally relaxed to a denser one. Around 7 GPa, the temperature-induced shift saturated and the crystallization temperature drastically increased. These results support the existence of a relatively stable high-pressure form of SiO
glass was measured at several pressures up to 19.2 GPa. The position of the first sharp diffraction peak moved to a higher momentum transfer as the temperature increased in a specific pressure-temperature range. The intermediate range structure was thermally relaxed to a denser one. Around 7 GPa, the temperature-induced shift saturated and the crystallization temperature drastically increased. These results support the existence of a relatively stable high-pressure form of SiO glass. A sudden transformation was not observed.
glass. A sudden transformation was not observed.
Endo, Akira; Kim, E.; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Yoshizawa, Michio; Tanaka, Susumu; Nakamura, Takashi; Rasolonjatovo, A. H. D.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.510 - 513, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
 Lu
Lu B
B C
C (0
(0 x
x 0.31) compounds
0.31) compoundsTobo, Aya*; Ishimoto, Kenichi*; Konno, Junya*; Oyama, Kenji*; Kaneko, Koji; Yamaguchi, Yasuo*; Onodera, Hideya*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 72(12), p.3231 - 3236, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.86(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Katayama, Yoshinori; Inamura, Yasuhiro
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 15(1), p.S343 - S350, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:61.19(Physics, Condensed Matter)Combination of synchrotron radiation sources and large volume presses enable us to make in-situ observations of structural change in liquids and glasses at high pressures up to several GPa and high temperatures up to 1500K. A number of methods, X-ray diffraction, XAFS, density measurement by means of X-ray absorption, viscosity measurements by means of radiography, are now applicable for this purpose. We have systematically studied elemental liquid and found that a characteristic structural change occurs in a narrow pressure-temperature range in liquid selenium. Moreover we have found a sudden structural change in liquid phosphorus. Experimental results on phosphorus support a view that the change is a first-order liquid-liquid transition. In the talk, results of current attempt to detect sudden structural change in silica glass will be presented. A preliminary result of X-ray diffraction study on liquid water under high-pressure will be also reported.
Dai, S.*; Sugiyama, Akira; Hu, L.*; Liu, Z.*; Huang, G.*; Jiang, Z.*
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 311(2), p.138 - 144, 2002/11
Low-temperature absorption and fluorescence spectra of the Yb3+ ions were measured in phosphate glass with compositions of (60-65)P O
O -(4-8)B
-(4-8)B O
O -(5-10)Al
-(5-10)Al O
O -(10-15)K
-(10-15)K O-(5-10)BaO-(0-2)La
O-(5-10)BaO-(0-2)La O
O -(0-2)Nb
-(0-2)Nb O
O -(4-87)Yb
-(4-87)Yb O
O in mol-%. Temperature dependence of lifetime from
in mol-%. Temperature dependence of lifetime from  F
F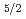 upper level of YB
upper level of YB was investigated with a cryostat. The glass laser performance pumped by 940 nm laser diode was measured at different temperature range. At 8 K, glass laser oscillation had a slope efficiency of 4% and a maximum power of 2 mW at the peak laser wavelength of 1001 nm.
was investigated with a cryostat. The glass laser performance pumped by 940 nm laser diode was measured at different temperature range. At 8 K, glass laser oscillation had a slope efficiency of 4% and a maximum power of 2 mW at the peak laser wavelength of 1001 nm.
 O
O crystals
crystalsKiriyama, Hiromitsu; Inoue, Norihiro*; Yamakawa, Koichi
JAERI-Research 2002-020, 13 Pages, 2002/09
no abstracts in English
 Li glass scintillator for wide energy range
Li glass scintillator for wide energy rangeKim, E.; Endo, Akira; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Yoshizawa, Michio; Nakamura, Takashi*; Rasolonjatovo, D. R. D.*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 1(3), p.317 - 319, 2002/09
no abstracts in English
To, Kentaro; Katagiri, Masaki; Sakasai, Kaoru; Matsubayashi, Masahito; Birumachi, Atsushi; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Nakazawa, Masaharu*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 485(3), p.571 - 575, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.91(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Kim, E.; Endo, Akira; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Yoshizawa, Michio; Tanaka, Susumu; Shiomi, T.*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Rasolonjatovo, D. R. D.*
JAERI-Tech 2002-041, 73 Pages, 2002/03
no abstracts in English